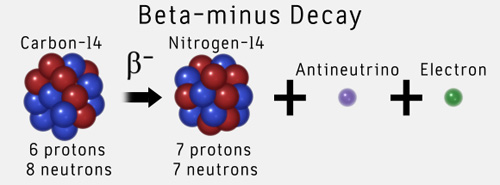
The stable form of carbon is carbon 12 and the radioactive isotope carbon 14 decays over time into nitrogen 14 and other particles. Archaeologists use the exponential radioactive decay of carbon 14 to estimate the death dates of organic material. Here is the equation for the alpha decay of radon 219 into polonium.

When a radioactive atom emits an alpha particle the mass number decreases by four and the atomic number drops by two. 614c 714n 10e where the e is an electron or beta particle. The equation for the beta decay of 14c.
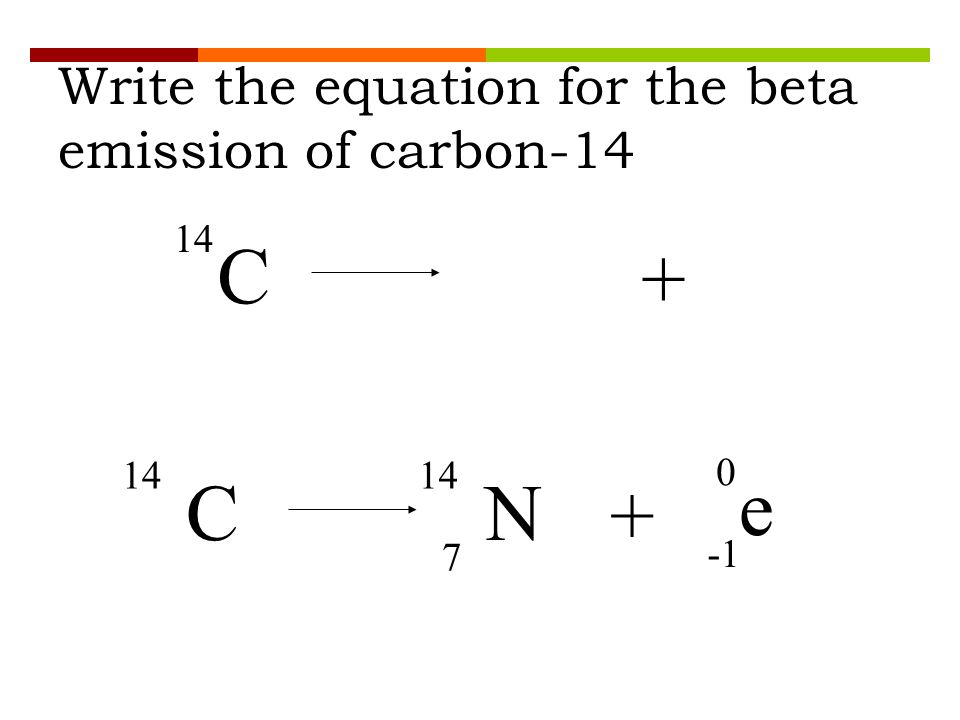
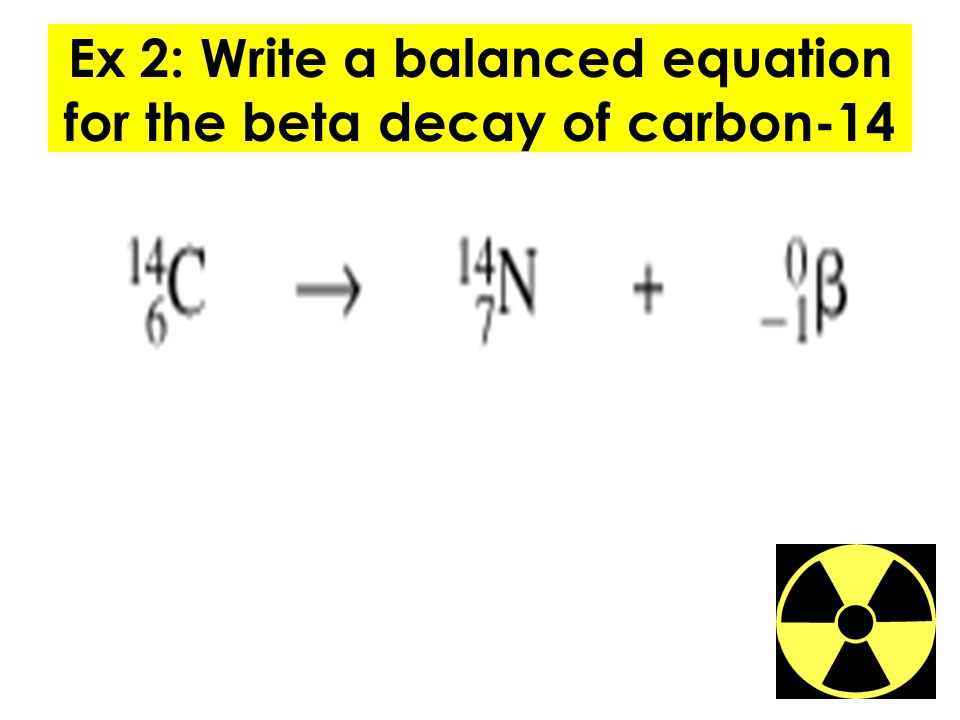
Here is the equation for the beta decay of carbon 14 into nitrogen. Here is the equation for the beta decay of carbon 14 into nitrogen. For example carbon 14 is a radioactive isotope.
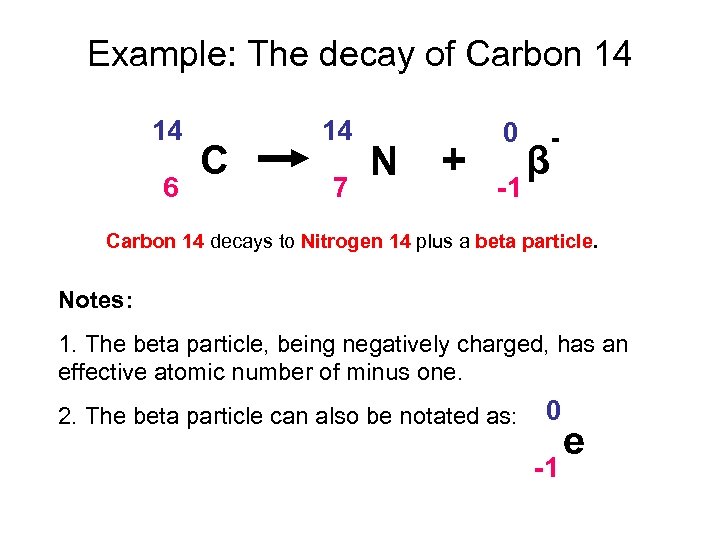
14 6 c 14 7 n β particle e. Carbon 14 decays by emitting beta particles and giving nitrogen. Carbon 14 14 6 c isotope is unstable and radioactive.

It has all the chemical properties similar to those shown by normal carbon 14 6 c. It is written as 14 6 c. Carbon 14 is an isotope of carbon.

Beta decay of c 14 nucleus. Radioactive carbon 14 has a half life of 5730 years and undergoes β decay where the neutron is converted into a proton an electron and an electron antineutrino. The only cosmogenic radionuclide to make a significant contribution to internal exposure of human is carbon 14.

The emitted beta particles have a maximum energy of 156.
Nuclear decay equation for carbon 14. The carbon 14 atoms undergo beta minus decay electron emission and produce a beta particle and a nitrogen 14 atom. A neutron in the atom undergoes decay and will produce a proton electron the beta particle and an electron antineutrino. Here s a video to give more explanation. Radioactive decay and detection.
Carbon 14 goes through radioactive beta decay. 14 6 c 14 7 n e ν e. By emitting an electron and an electron antineutrino one of the neutrons in the carbon 14 atom decays to a proton and the carbon 14 half life of 5 700 40 years decays into the stable non radioactive isotope nitrogen 14.
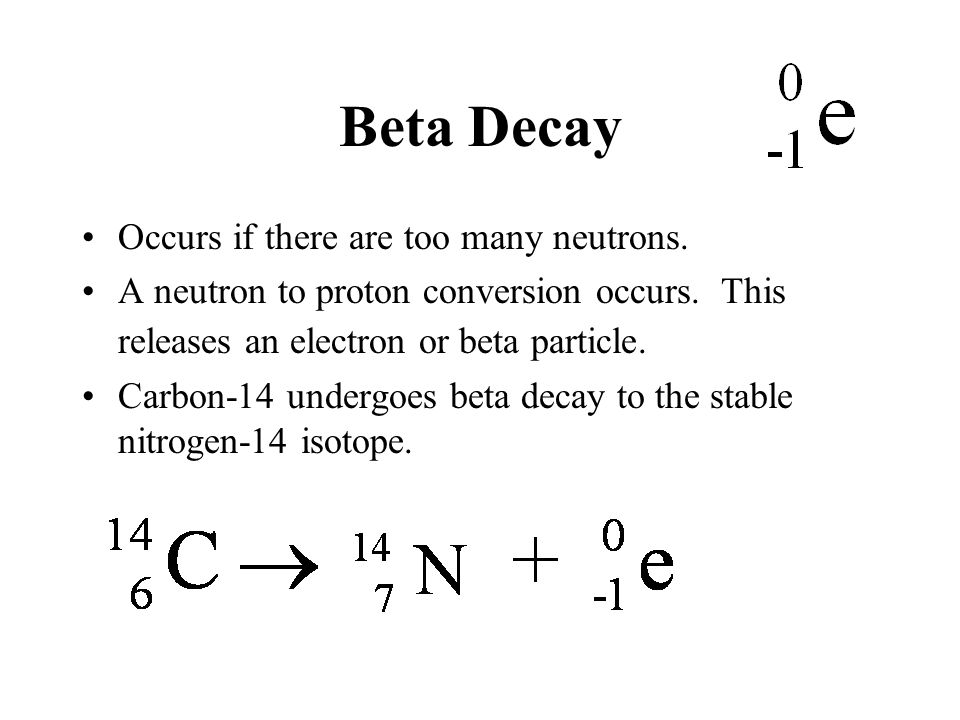
By emitting an electron and an electron antineutrino one of the neutrons in the carbon 14 atom decays to a proton and the carbon 14 half life of 5 700 40 years decays into the stable non radioactive isotope nitrogen 14. 14 6 c 14 7 n e ν e. Carbon 14 goes through radioactive beta decay.

Radioactive decay and detection. Here s a video to give more explanation. A neutron in the atom undergoes decay and will produce a proton electron the beta particle and an electron antineutrino.
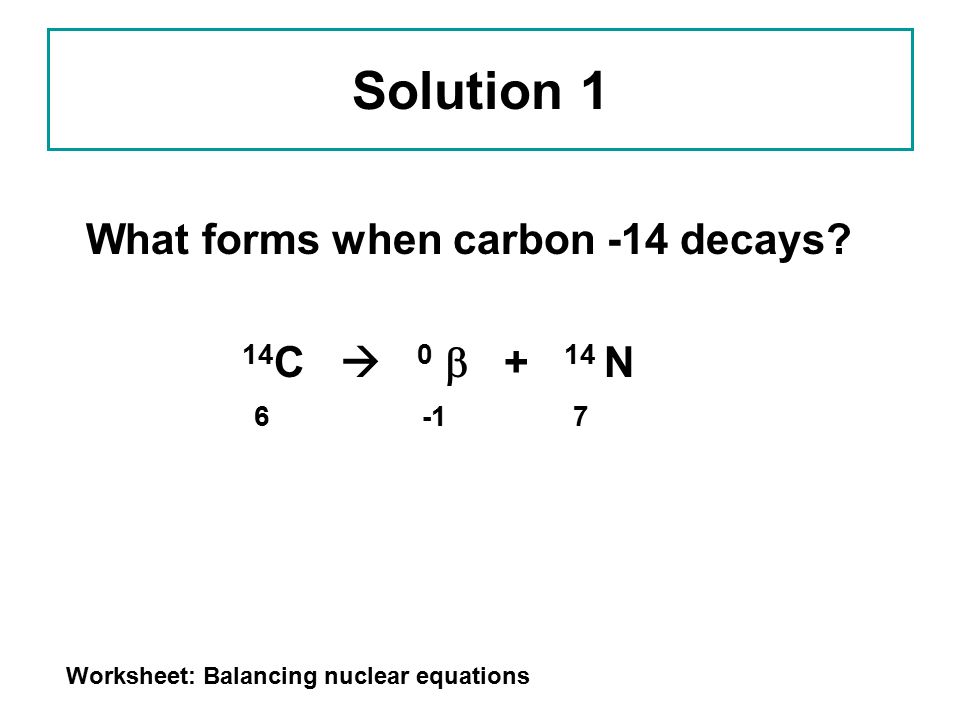
The carbon 14 atoms undergo beta minus decay electron emission and produce a beta particle and a nitrogen 14 atom.