The fusion of nuclei in a star starting from its initial hydrogen and helium abundance provides that energy and synthesizes new nuclei as a byproduct of that fusion. In the 20th century it was realized that the energy released from nuclear fusion reactions accounted for the longevity of the sun and other stars as a source of heat and light. Inside the sun this process begins with protons which is simply a lone hydrogen nucleus and through a series of steps these protons fuse together and are.

The energy from the sun both heat and light energy originates from a nuclear fusion process that is occurring inside the core of the sun the specific type of fusion that occurs inside of the sun is known as proton proton fusion. Energy is generated in this central region and keeps it hot. This reaction only occurs in the central regions of the sun where it is hottest.

In the sun the nuclear reaction which occurs is called the proton proton cycle in which four hydrogen atoms are combined in a series of reactions to from one helium atom. The sun s energy is from star formation the sun keeps the same amoun. Energy can only co exist with matter.

Energy cannot vanish into space. The sun does not radiate energy into space. The truth of the sun the sun is not an ongoing fusion reactor.

Nuclear reactions in the sun core 15 million o k photosphere visible surface 5700 o k photons no longer collide can escape chromosphere 10 000 o k corona 2 million o k low density but high temperature due to magnetic fields and violent convective motions of lower layers source of x rays. Absent these nuclear reactions earth would be a cold and dark world devoid of life. Deep within the sun high temperatures and pressures drive the fusion of hydrogen into helium.

A positron and a neutrino. Two additional particles are released. Because this chain of reactions starts with two hydrogen nuclei that is two single protons it is called the proton proton chain in step 1 two protons collide and fuse forming deuterium which is designated 2 h or d.

The principal nuclear reactions inside the sun convert hydrogen into helium in three stages.
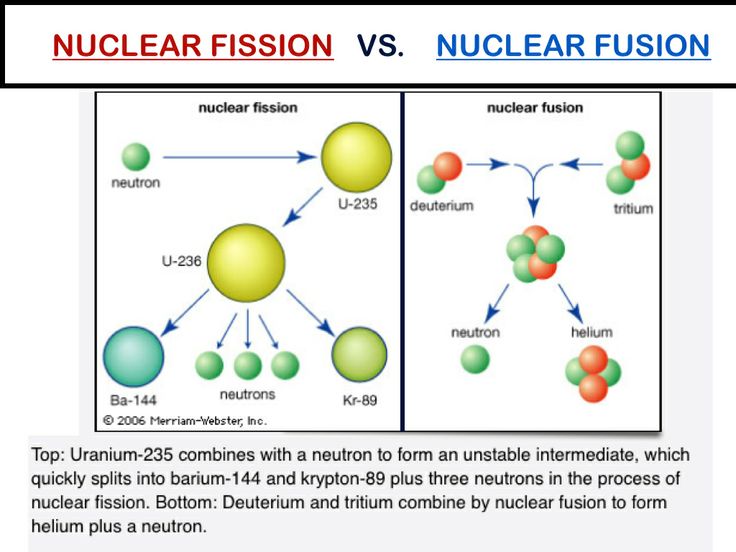
Nuclear reaction in sun. In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry a nuclear reaction is semantically considered to be the process in which two nuclei or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle collide to produce one or more new nuclides thus a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another. If a nucleus interacts with another nucleus or particle and they then separate without. Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles neutrons or protons the difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption of energy this difference in mass arises due to the difference in atomic binding energy between the atomic nuclei. The type of nuclear fusion reactions that occur inside a star are entirely dependent on the core temperature.
In the sun with a core temperature close to 15 6 million kelvin the predominant pathway by which more than 99 of solar energy is produced through conversion of hydrogen into helium nuclei is the proton proton p p chain reaction.

In the sun with a core temperature close to 15 6 million kelvin the predominant pathway by which more than 99 of solar energy is produced through conversion of hydrogen into helium nuclei is the proton proton p p chain reaction. The type of nuclear fusion reactions that occur inside a star are entirely dependent on the core temperature. Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles neutrons or protons the difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption of energy this difference in mass arises due to the difference in atomic binding energy between the atomic nuclei.

If a nucleus interacts with another nucleus or particle and they then separate without. In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry a nuclear reaction is semantically considered to be the process in which two nuclei or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle collide to produce one or more new nuclides thus a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another.