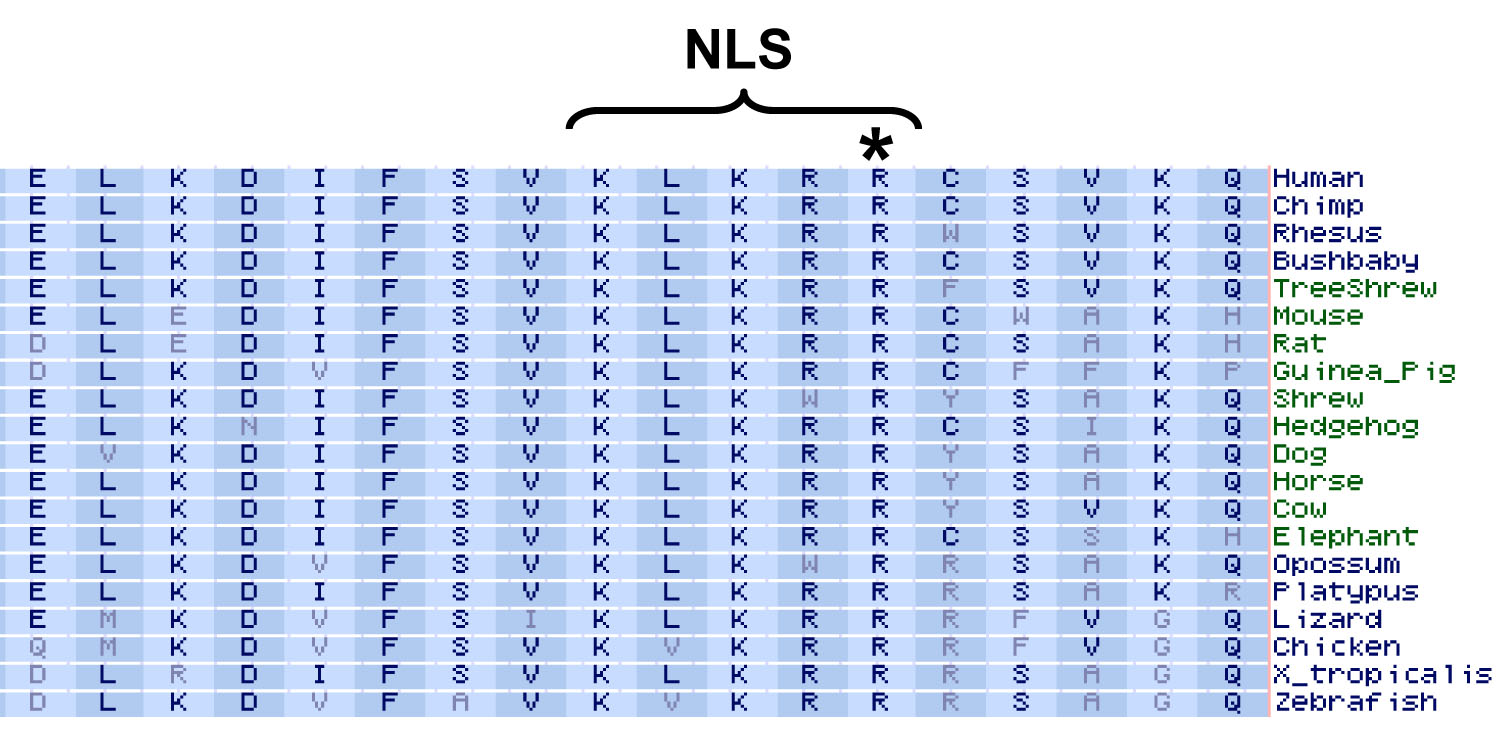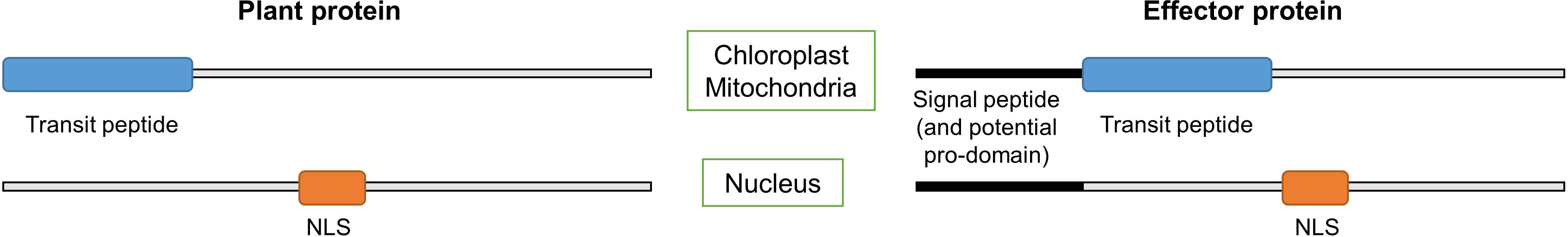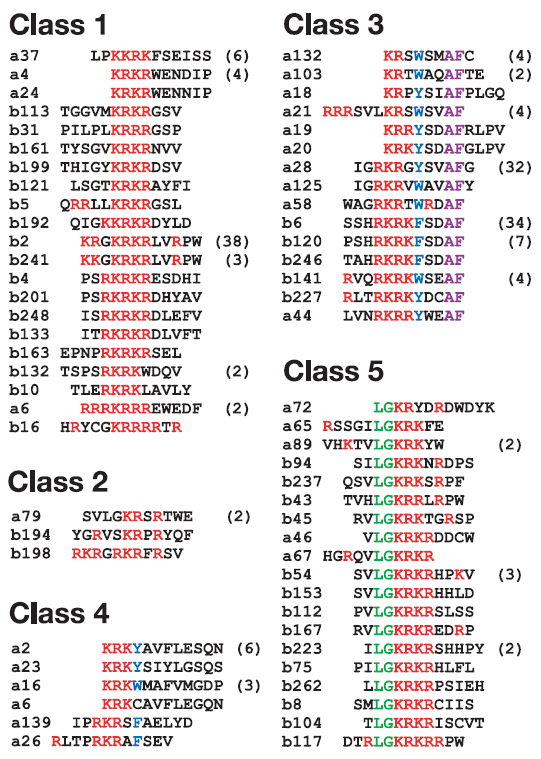
It often consists of several hydrophobic amino acids. A nuclear export signal nes is a target peptide that directs proteins from the nucleus back to the cytosol. The nls normally is located anywhere on the peptide chain.

A nuclear localization signal nls is a target peptide that directs proteins to the nucleus and is often a unit consisting of five basic positively charged amino acids. 0 1 0 3 0 5 0 7 0 8 0 86 0 89 default 0 86 receive prediction results by e mail e mail address. No more than 20 sequences a time final score cutoff.

Please paste protein sequence s in fasta format. Nuclear localization signal prediction based on frequent pattern mining and linear motif scoring. Has a consensus basic amino acid residue sequence kkkrk is recognized by a nuclear import receptor protein that is a nuclear membrane bound protein close to the nuclear pore complexes has a consensus acidic amino acid residue sequence kkkrk.

The nls nuclear localization signal sequence. Choose all that apply. 2 a spacer region of any 10 residues.

1 two adjacent basic amino acids arg or lys. Although some consensus sequence patterns have been proposed see for example the current best strategy to detect a nuclear targeting sequence is based on the following definition of what is called a bipartite nuclear localization signal. I need to find out the nuclear localization signal sequences nls for mda mb 231 breast cancer cell line against qw10 qqwqqqqwqq peptide sequence.

Spriyansh29 30 wrote. 7 months ago by. Nuclear localization signal sequences nls prediction.

Nls peptide nuclear localization signal peptide nuclear localization signals chemical ingredient expand short predominantly basic amino acid sequences identified as nuclear import signals for some proteins.
Nuclear localization signal sequence. A nuclear localization signal or sequence nls is an amino acid sequence that tags a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport typically this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines or arginines exposed on the protein surface. Different nuclear localized proteins may share the same nls. Nuclear localization signal binding assay. Nls peptides and reverse sequence nls peptides were conjugated to bovine serum albumin bsa.
Biotin was coupled to the conjugated proteins. 2 mg ml of reverse sequence nls bsa was added to 100 μl of hss followed by the addition of 40 μg ml biotinylated nls bsa. D nuclear localization signal nls sequences. Nls sequences are typically short peptide sequences responsible for direct import of proteins into the nucleus.
In general these sequences contain a high proportion of the basic amino acids lysine and arginine lanford and butel 1984. Frequently amino acids such as proline which disrupt. Classical nuclear localization signal. The first step of nuclear import occurs when an importin discriminates between its cargo and other cellular proteins.
Proteins destined for transport into the nucleus contain amino acid targeting sequences called n uclear l ocalization s ignals nlss.

Proteins destined for transport into the nucleus contain amino acid targeting sequences called n uclear l ocalization s ignals nlss. The first step of nuclear import occurs when an importin discriminates between its cargo and other cellular proteins. Classical nuclear localization signal.

Frequently amino acids such as proline which disrupt. In general these sequences contain a high proportion of the basic amino acids lysine and arginine lanford and butel 1984. Nls sequences are typically short peptide sequences responsible for direct import of proteins into the nucleus.

D nuclear localization signal nls sequences. 2 mg ml of reverse sequence nls bsa was added to 100 μl of hss followed by the addition of 40 μg ml biotinylated nls bsa. Biotin was coupled to the conjugated proteins.

Nls peptides and reverse sequence nls peptides were conjugated to bovine serum albumin bsa. Nuclear localization signal binding assay. Different nuclear localized proteins may share the same nls.
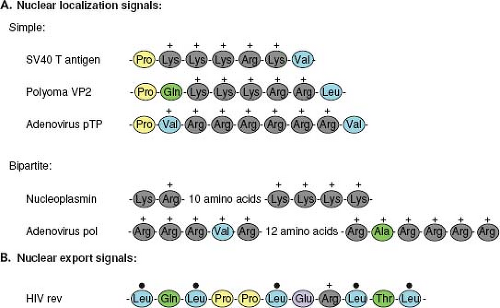
A nuclear localization signal or sequence nls is an amino acid sequence that tags a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport typically this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines or arginines exposed on the protein surface.