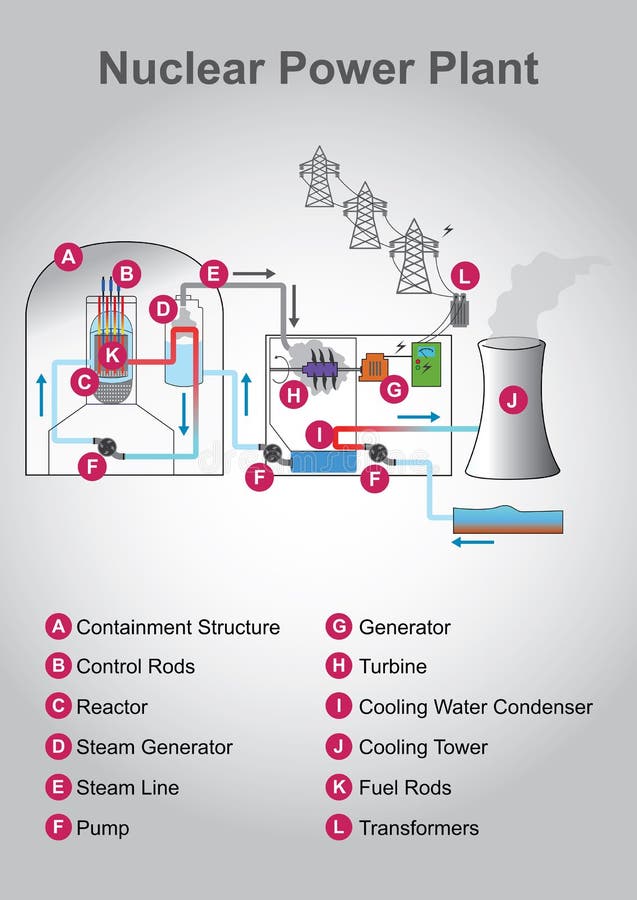
The number of control rods inserted and the distance to which they are inserted strongly influence the reactivity of the. Control rods are inserted into the core of a nuclear reactor and adjusted in order to control the rate of the nuclear chain reaction and thereby the thermal power output of the reactor the rate of steam production and the electrical power output of the power station. An uncontrolled chain reaction is carried out in the absence of moderators.

A controlled chain reaction is carried out in the presence of moderators. An uncontrolled chain reaction is a chain of nuclear reactions that take place subsequently but not under controlled conditions. Too few fission events can slow down and ultimately stop the chain reaction.
The key to generating a steady output of energy is controlling the nuclear fission inside a reactor core. The control rods are also used to shut down the reactor and can stop a nuclear chain reaction within 2 seconds. The control rods in a nuclear reactor are used to control the speed of the chain reaction and can capture free neutrons before they collide with u235 atoms.

In a reactor the propagation of fissions takes place in a controlled manner in a nuclear weapon in an uncontrolled explosive manner. It is the chain reaction process that is used in reactors and nuclear weapons to generate a large number of fissions. This causes the nucleus to.

In a nuclear reactor a neutron is absorbed into a nucleus typically uranium 235. Nuclear fission is the splitting of a large atomic nucleus into smaller nuclei. It was pointed out in the preceding articles that the neutron induced fission reaction is the reaction in which the incident neutron enters the heavy target nucleus fissionable nucleus forming a compound nucleus that is excited to such a high energy level e excitation e critical that the nucleus splits into two large fission fragments.
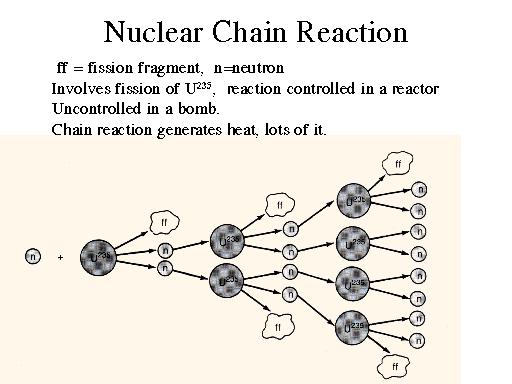
For example 212 neutrons on the average are released by the fission of each uranium 235 nucleus that absorbs a low energy neutron. Nuclear chain reactions are series of nuclear fissions splitting of atomic nuclei each initiated by a neutron produced in a preceding fission. Other articles where nuclear chain reaction is discussed.

The nuclear chain reaction releases several million times more energy per reaction than any.
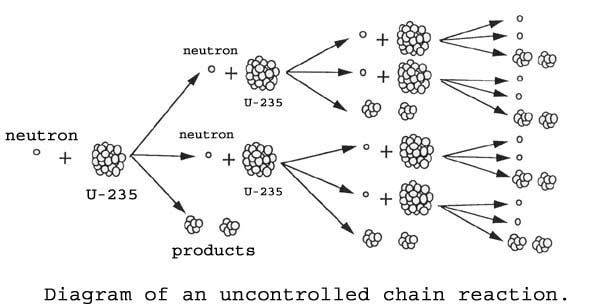
Uncontrolled nuclear chain reaction diagram. Nuclear fission nuclear fission fission chain reactions and their control. The emission of several neutrons in the fission process leads to the possibility of a chain reaction if at least one of the fission neutrons induces fission in another fissile nucleus which in turn fissions and emits neutrons to continue the chain. If more than one neutron is effective in inducing fission in other. Nuclear chain reaction occurs when one single nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more subsequent nuclear reactions thus leading to the possibility of a self propagating series of these reactions.
The specific nuclear reaction may be the fission of heavy isotopes e g uranium 235 235 u.

The specific nuclear reaction may be the fission of heavy isotopes e g uranium 235 235 u. Nuclear chain reaction occurs when one single nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more subsequent nuclear reactions thus leading to the possibility of a self propagating series of these reactions. If more than one neutron is effective in inducing fission in other.

The emission of several neutrons in the fission process leads to the possibility of a chain reaction if at least one of the fission neutrons induces fission in another fissile nucleus which in turn fissions and emits neutrons to continue the chain. Nuclear fission nuclear fission fission chain reactions and their control.