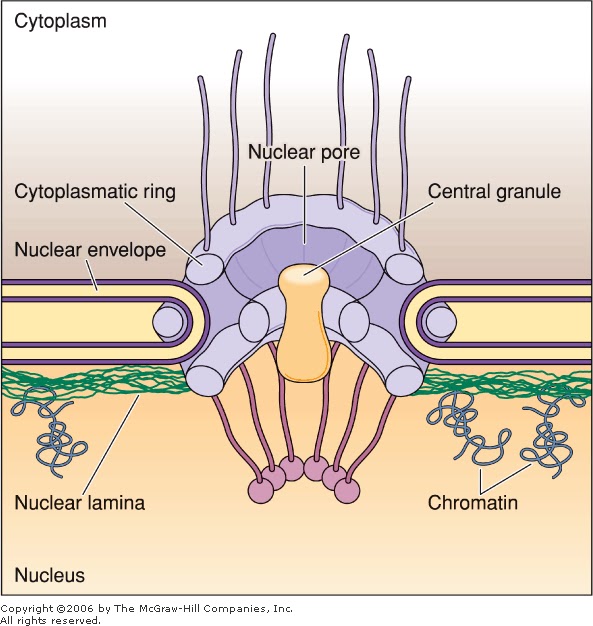
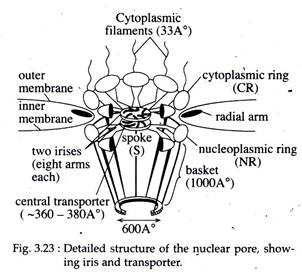
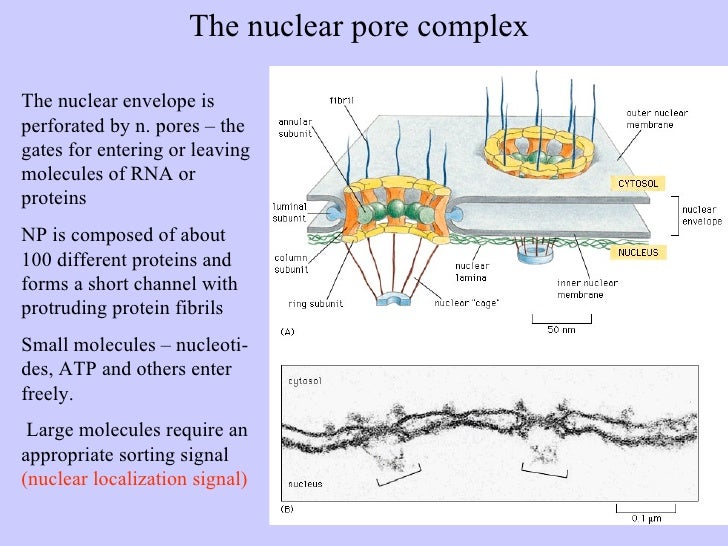
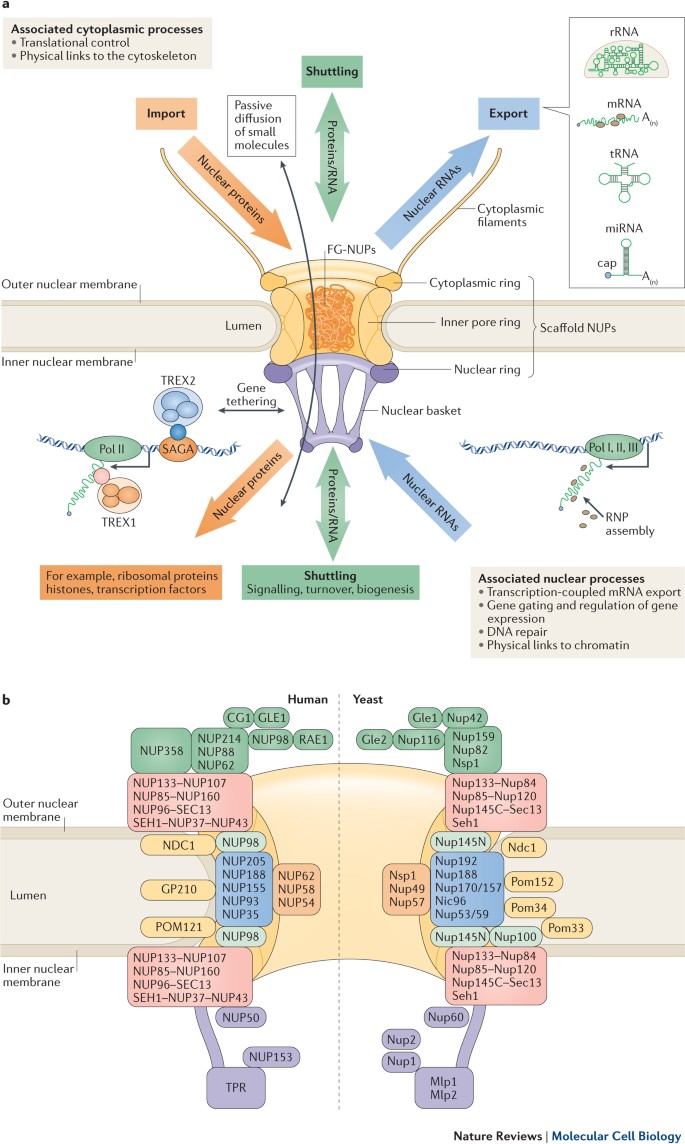
A key component of the npc is the central shaft lined with intrinsically disordered proteins idps known as fg nups which control the selective molecular traffic. The nuclear pore complex npc is the gatekeeper for nuclear transport in eukaryotic cells. In order to investigate the chemical composition of the nuclear pore complexes.
Scheer department of cell biology institute of biology ii university of freiburg i br germany received november 25 1971 summary. On the chemical nature of the nuclear pore complex material u. The ultrastructure of the nuclear envelope of amphibian oocytes iv.
We used molecular modeling combined with cross linking mass spectrometry and cryo electron tomography to obtain a composite structure of the inner ring. However the organization of the inner ring has remained unknown until now. Recently it has been shown how the y complex a prominent npc module forms the outer rings of the nuclear pore.

More than 40 years ago. Because the nuclear pore complexes npcs are the largest macromolecular complexes in cells early studies of the complexes in plants were performed using electron microscopy. Ultrastructure of the plant npc.
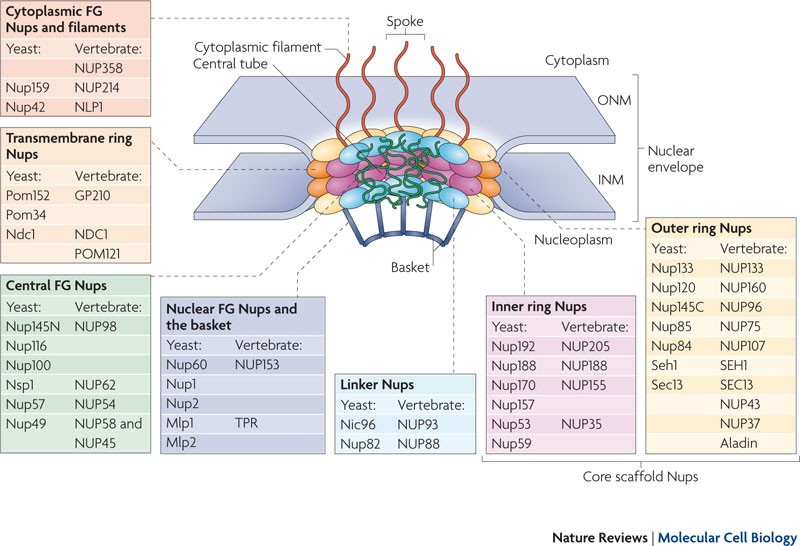
The combination of these methods can reveal new insights into the structural and functional organization of this important supramolecular machine through which. To study the ultrastructure of nuclear pore complexes npcs a wide spectrum of different electron microscopy em or atomic force microscopy afm techniques can be employed. The npc serves as a barrier to inhibit the free molecular flux in and out of the nucleus and selectively transports macromolecules.
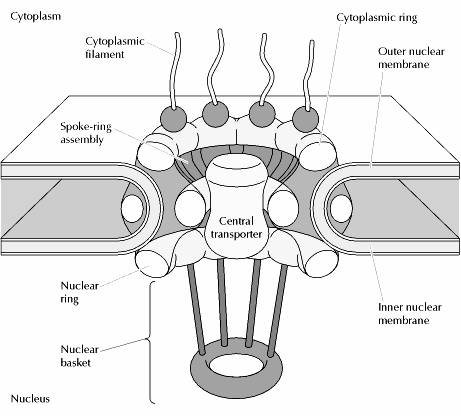
The nuclear pore complex npc is a macromolecular protein assembly embedded in the double lipid bilayer of the nuclear membrane and is the sole gateway of macromolecular traffic between the nucleus and cytoplasm. To acquire a deeper understanding of this transport mechanism we analyse the structure of the npc scaffold and permeability barrier by reconstructing the xenopus laevis oocyte npc from native nuclear. Nuclear pore complexes npcs perforate the nuclear envelope and allow the exchange of macromolecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.

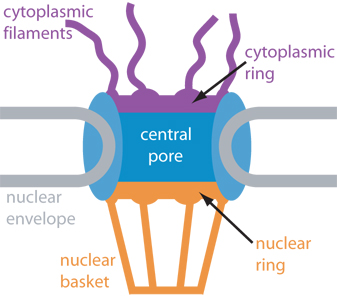
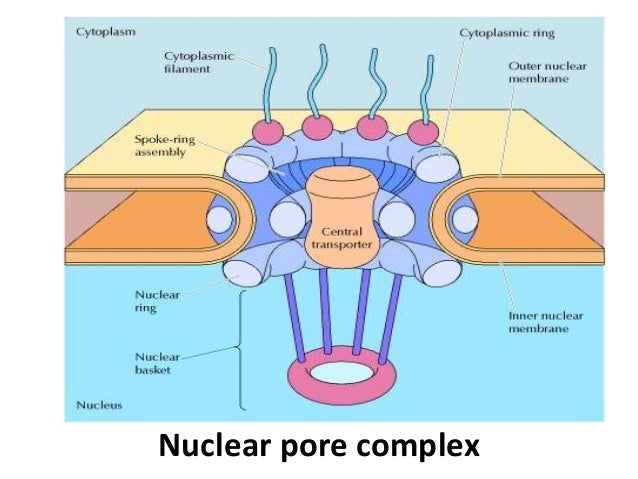
Npcs have an elaborate architecture that has been well studied in vertebrates.
Ultrastructure nuclear pore complex. Nuclear pore complexes npcs perforate the double layered nuclear envelope and form the main gateway for molecular exchange between nucleus and cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell. Because npcs are extraordinarily complex and large thus challenging to investigate on a molecular level they are still rather poorly understood despite their. 3d ultrastructure of the nuclear pore complex. Bilokapic s 1 schwartz tu.
Nuclear pore complexes npcs perforate the double layered nuclear envelope and form the main gateway for molecular exchange between nucleus and cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell. Because npcs are extraordinarily complex and large thus challenging to investigate on. Nuclear pore complexes npcs span the nuclear envelope and mediate nucleocytoplasmic exchange. They are a hallmark of eukaryotes and deeply rooted in the evolutionary origin of cellular compartmentalization.

They are a hallmark of eukaryotes and deeply rooted in the evolutionary origin of cellular compartmentalization. Nuclear pore complexes npcs span the nuclear envelope and mediate nucleocytoplasmic exchange. Because npcs are extraordinarily complex and large thus challenging to investigate on.

Nuclear pore complexes npcs perforate the double layered nuclear envelope and form the main gateway for molecular exchange between nucleus and cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell. Bilokapic s 1 schwartz tu. 3d ultrastructure of the nuclear pore complex.

Because npcs are extraordinarily complex and large thus challenging to investigate on a molecular level they are still rather poorly understood despite their. Nuclear pore complexes npcs perforate the double layered nuclear envelope and form the main gateway for molecular exchange between nucleus and cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell.