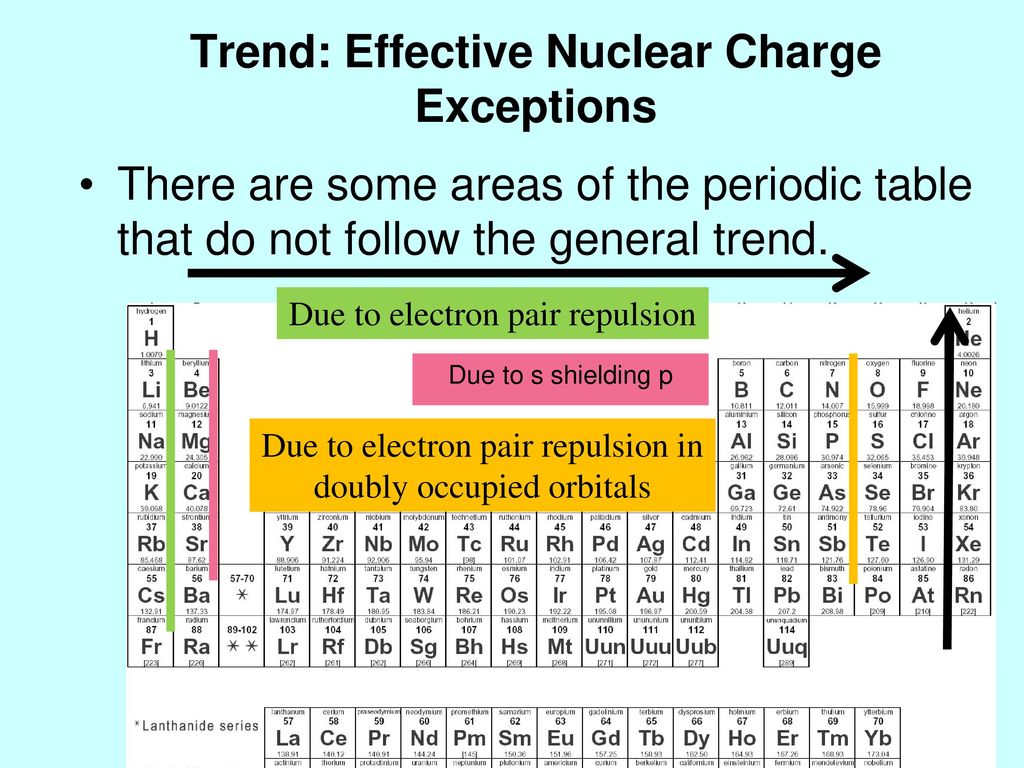
Write its configuration first. How many shielding electrons does carbon have. Play this game to review periodic table.

It increases across a period because putting more electrons in the same energy level doesn t pr. This is because the extra electron shells provide more shielding. It decreases down a group which is why fluorine is more electronegative than iodine.

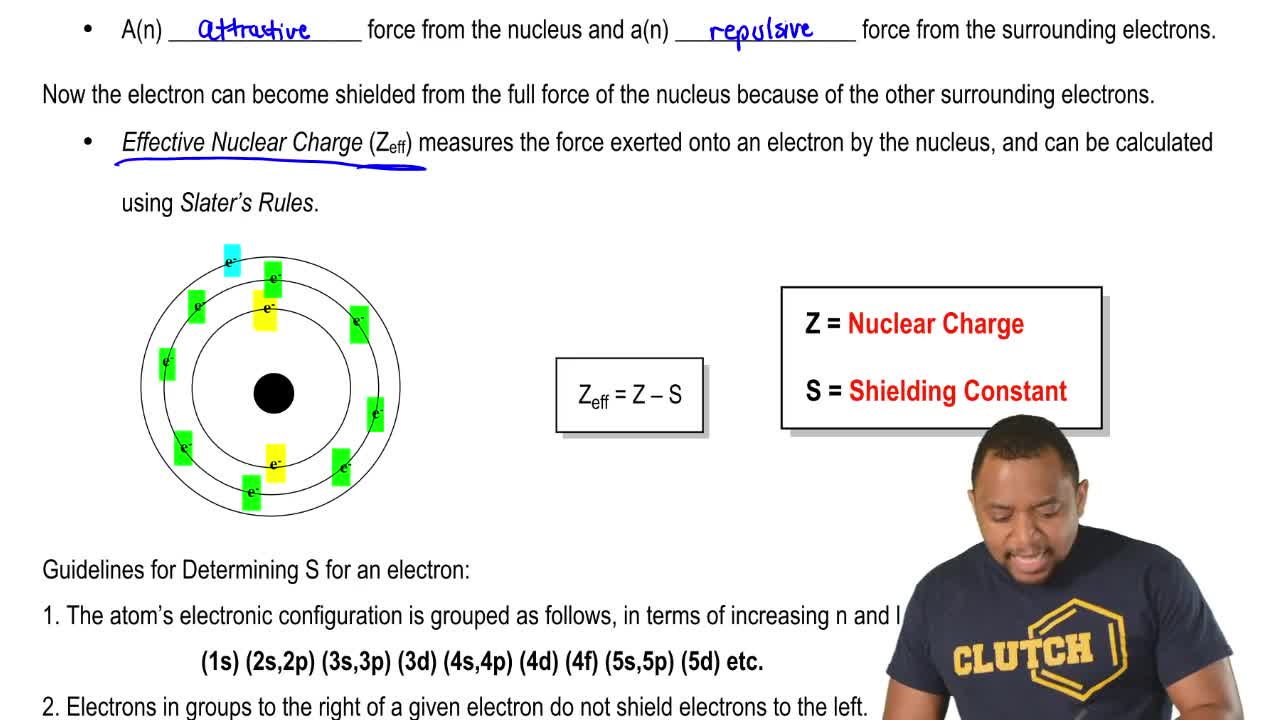
This video is a crash course on what shielding is what effective nuclear charge is how they are related how they produce specific atomic properties including the size of atoms and trends in. Relate these trends to effective nuclear charge and atomic size. Electrons in the same group contribute 0 35 to the shielding except the 1s group where a contribution of 0 30 is used.
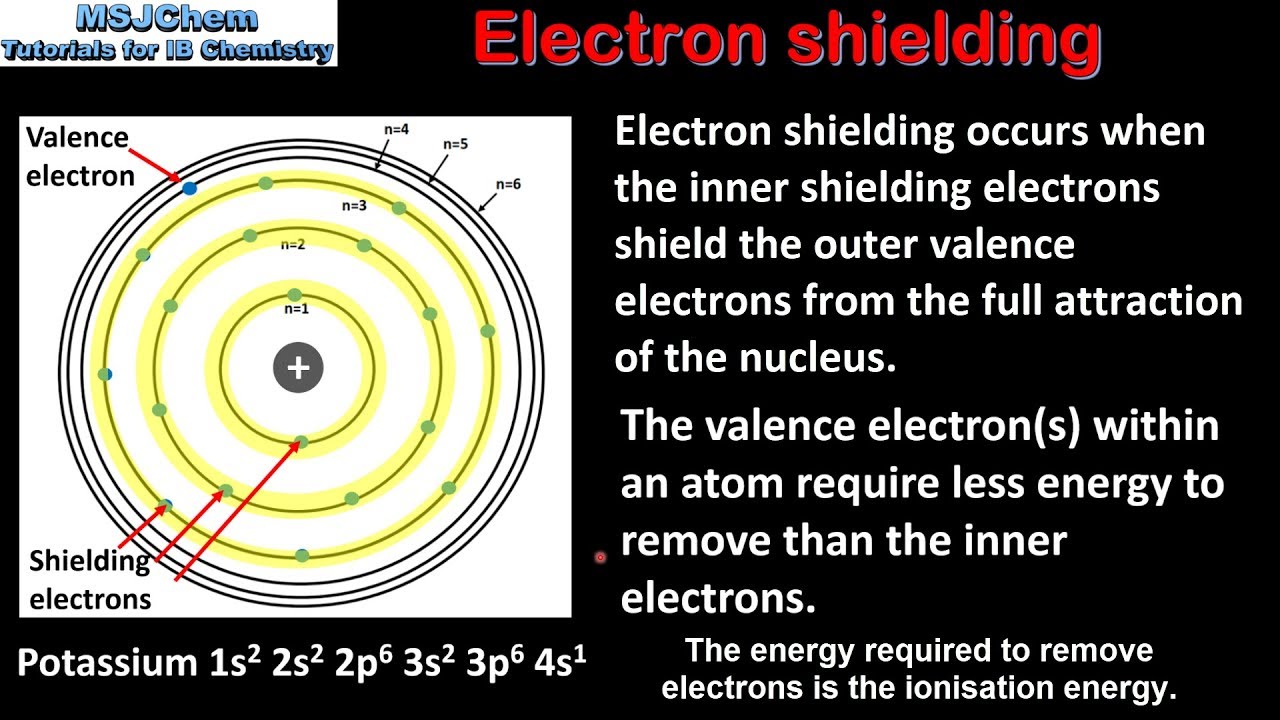
The amount of positive charge that actually acts on an electron is called the effective nuclear charge. The shielding effect sometimes referred to as atomic shielding or electron shielding describes the attraction between an electron and the nucleus in any atom with more than one electron the shielding effect can be defined as a reduction in the effective nuclear charge on the electron cloud due to a difference in the attraction forces on the electrons in the atom. The effective nuclear charge often symbolized as or is the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a polyelectronic atom the term effective is used because the shielding effect of negatively charged electrons prevents higher orbital electrons from experiencing the full nuclear charge of the nucleus due to the repelling effect of inner layer electrons.

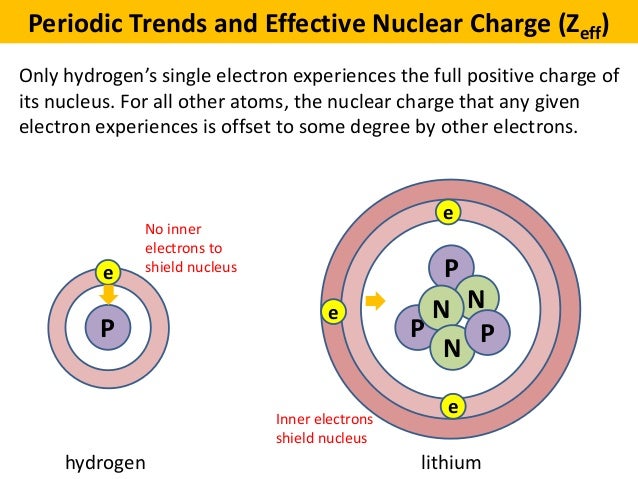
Hence the electrons will cancel a portion of the positive charge of the nucleus and thereby decrease. If an electron is far from the nucleus i e if the distance r between the nucleus and the electron is large then at any given moment many of the other electrons will be between that electron and the nucleus figure pageindex 1. Electron shielding and effective nuclear charge.
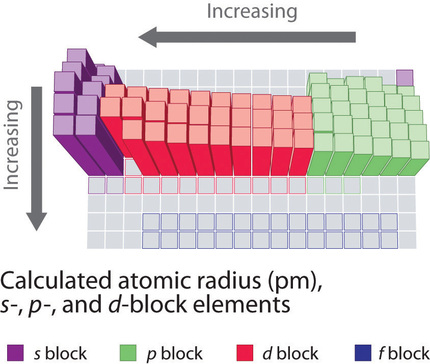
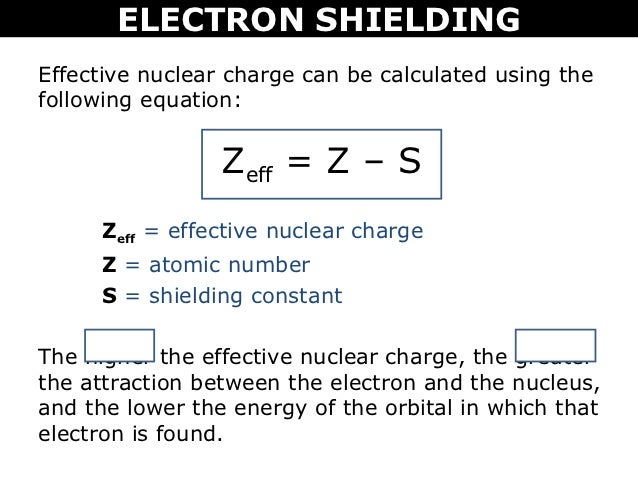
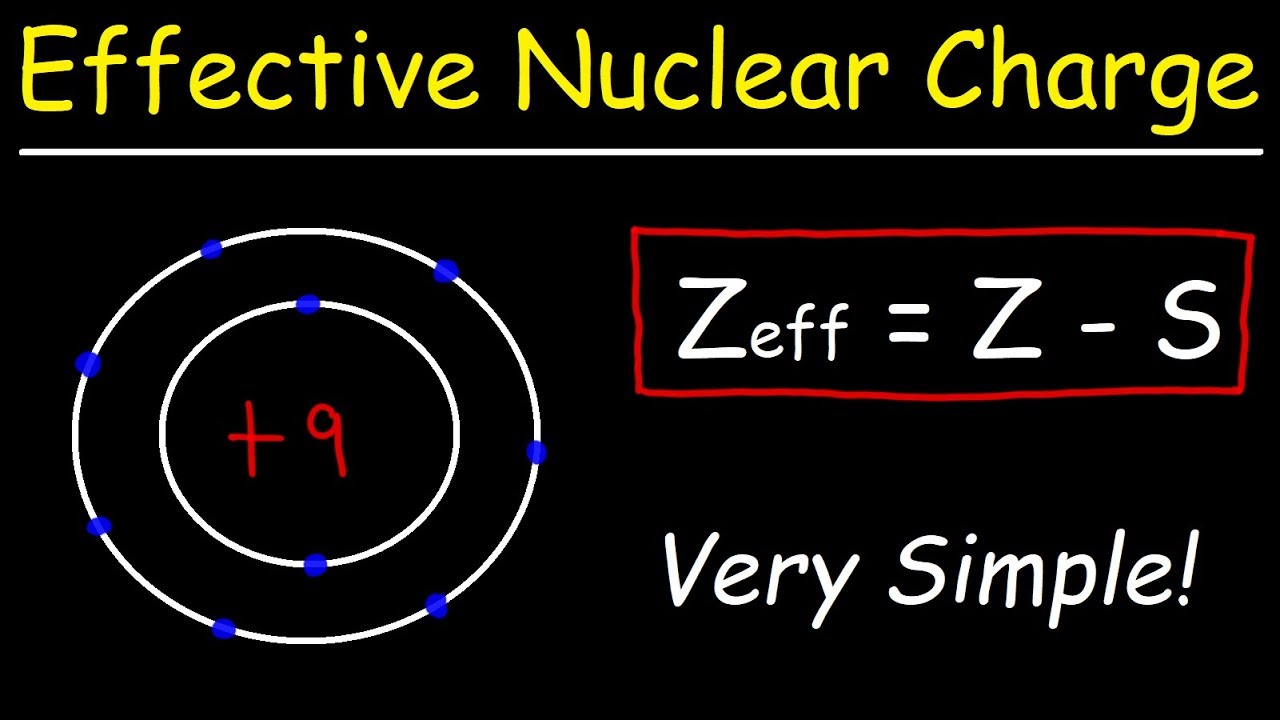
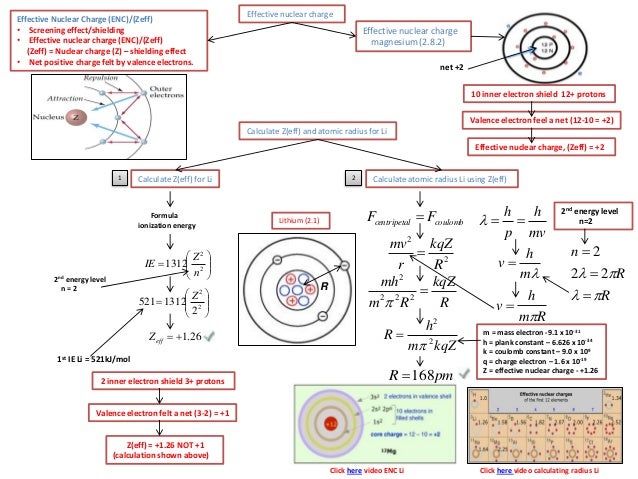
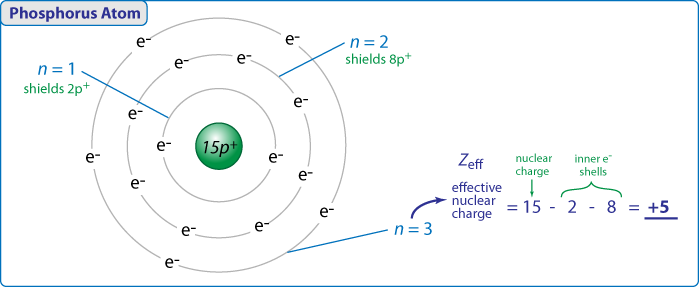
We can calculate an effective nuclear charge by using z effective z s where z is the atomic number and s is the number of shielding electrons. The term effective is used because the shielding effect of negatively charged electrons prevents higher orbital electrons from experiencing the full nuclear charge. The effective nuclear charge often symbolized as z eff or z is the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a multi electron atom.
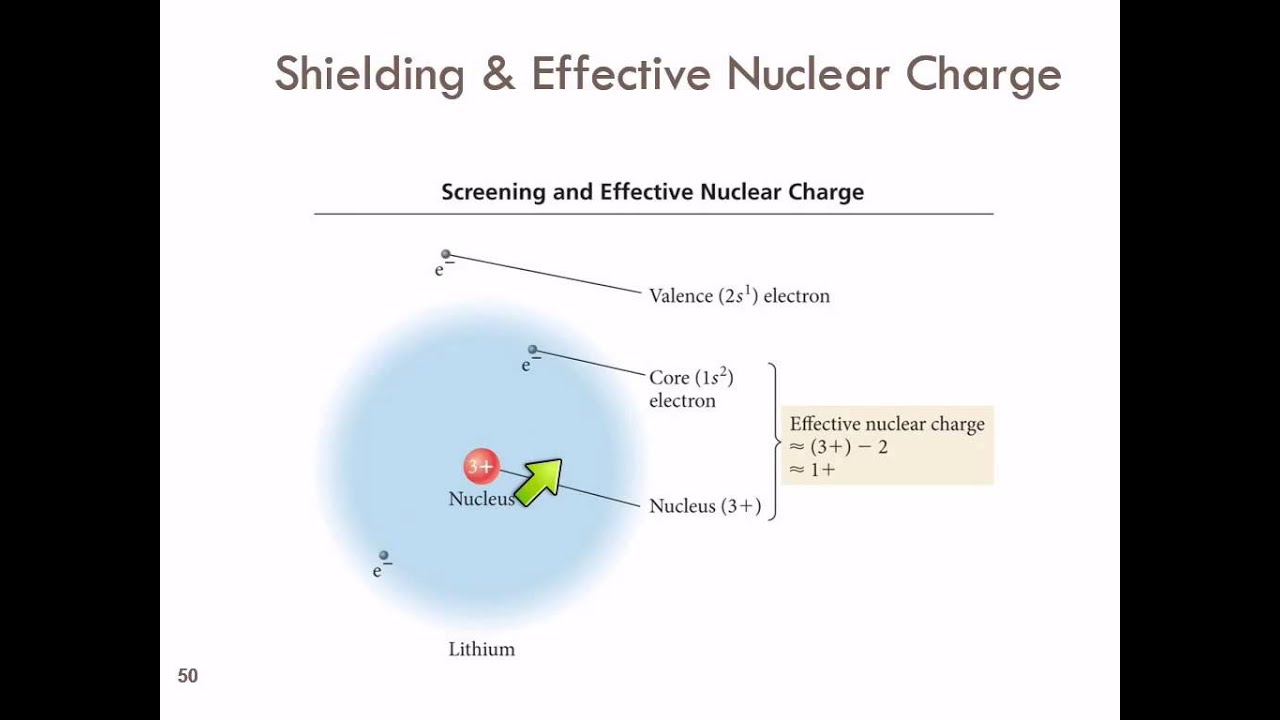
The concept of electron shielding in which intervening electrons act to reduce the positive nuclear charge experienced by an electron allows the use of hydrogen like orbitals and an effective nuclear charge z eff to describe electron distributions in more complex atoms or ions.