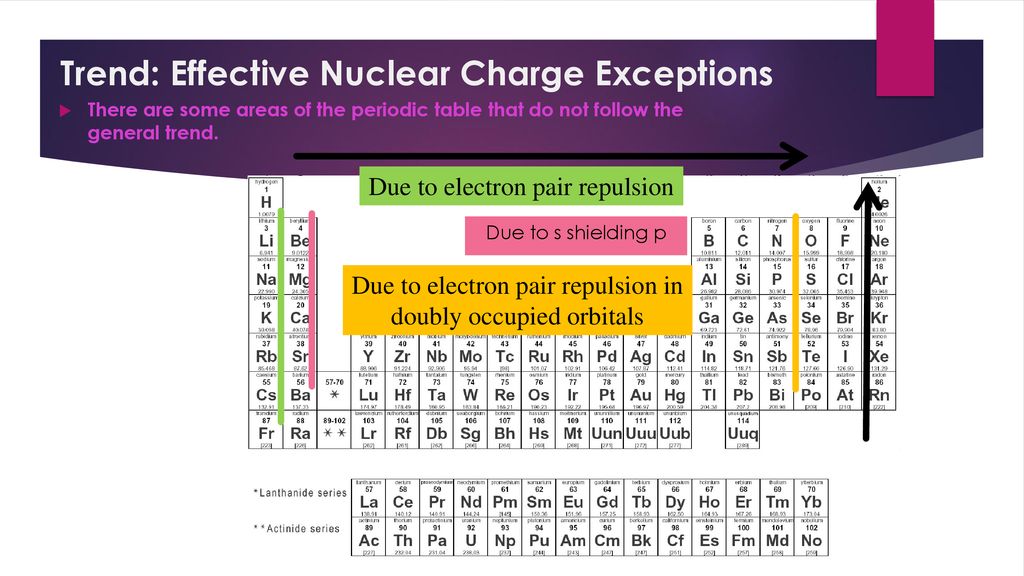
This is because the outermost electron is on average farther from the nucleus meaning it is held less tightly and requires less energy to remove. On the periodic table first ionization energy generally decreases as you move down a group. An element s first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost or least bound electron from a neutral atom of the element.

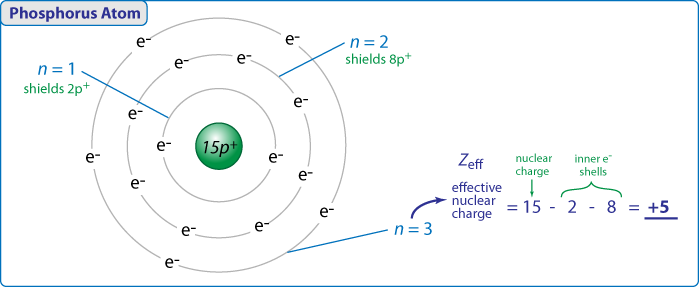
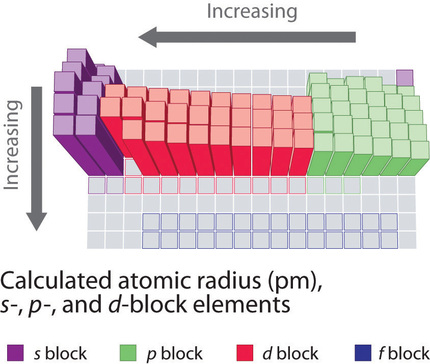
The electron configuration of argon is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6ar4 1s2 2s22p6 3s23p2 3 other 3s 3p electrons 3 x 0 35 1 05 8 2s 2p electrons 8 x 0 85 6 80 2 1s electrons 2 x 1 00 2 s 1 05 6 80 2 9 85 zeff. Periodic trends and zeffexample 1 calculate the effective nuclear charge of theoutermost electron in the following. The trend on the periodic table is to increase across a period and increase down a group.
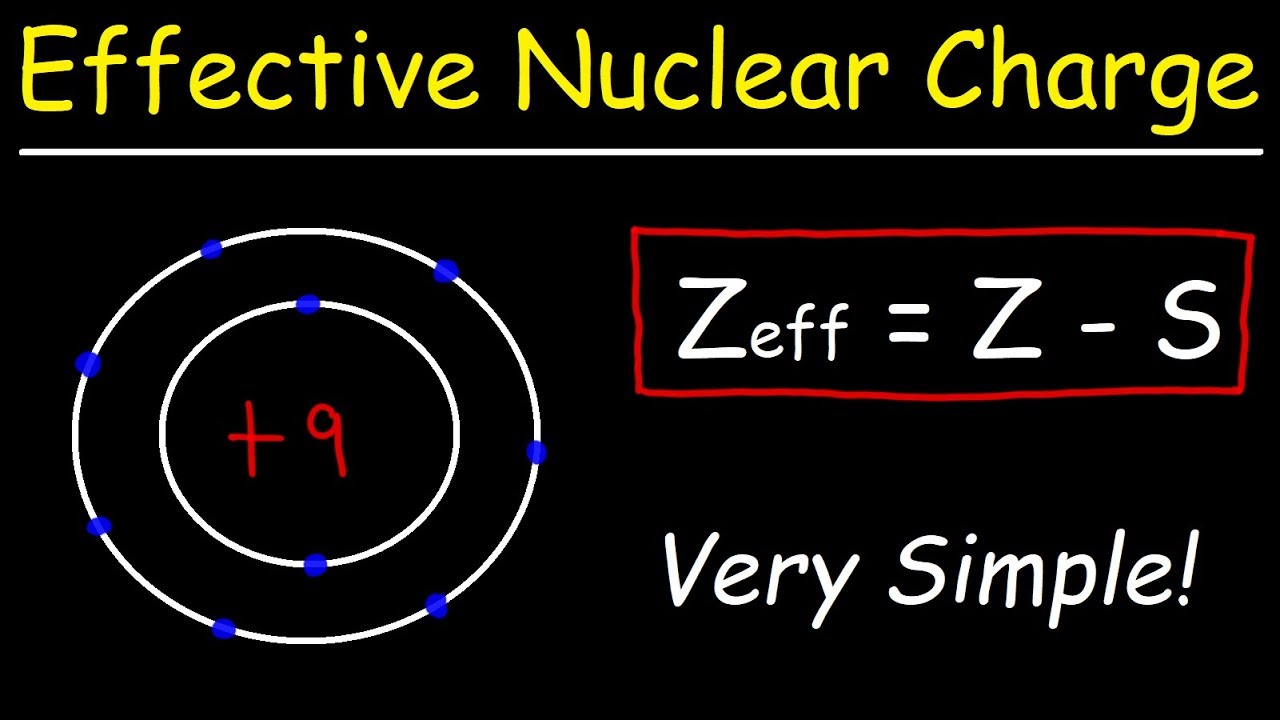
Effective nuclear charge refers to the charge felt by the outermost valence electrons of a multi electron atom after the number of shielding electrons that surround the nucleus is taken into account. Show transcribed image text. This problem has been solved.
View available hint s atomic size lonization energy electron affinity o all of the answers are correct. Part a which of the following trends is inversely proportional to effective nuclear charge zeff. Therefore using the equation for effective nuclear charge z eff z σ we see that bromine has a greater effective nuclear charge than potassium and that this trend is expected across the whole periodic table.
Bromine has 35 protons. The shielding effect explains the trend in atomic size on the periodic table and also why valence electrons are readily removed from an atom. The shielding effect is the name given to the balance between the attraction between valence electrons and protons and the repulsion between valence and inner electrons.
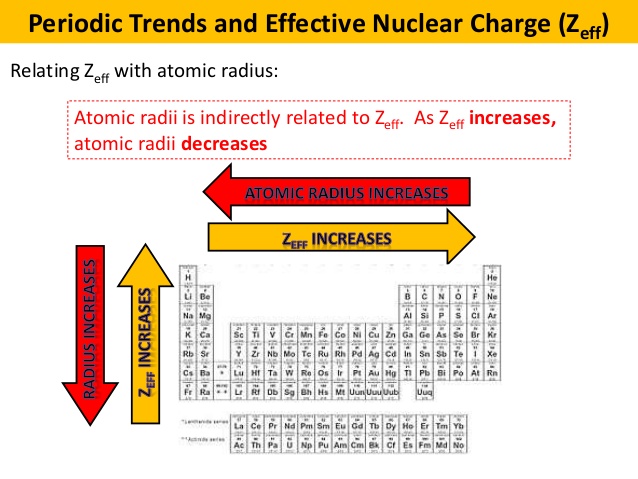
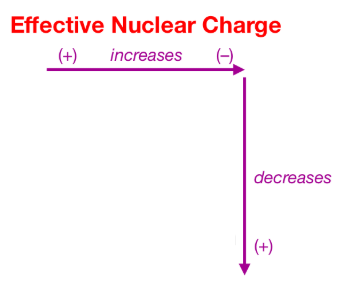
As zeff increases atomic radii decreases 14. Atomic radii is indirectly related to zeff. Periodic trends and effective nuclear charge zeff relating zeff with atomic radius.
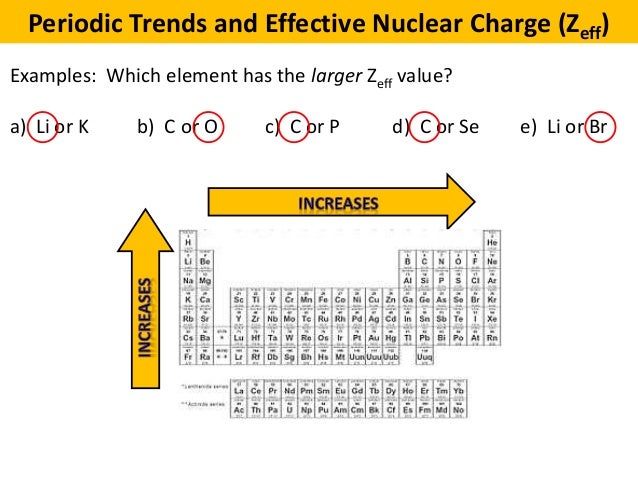
A li or k b c or o c c or p d c or se e li or br 13.
Zeff nuclear charge trend. Consequently the ion with the greatest nuclear charge al 3 is the smallest and the ion with the smallest nuclear charge n 3 is the largest. The neon atom in this isoelectronic series is not listed in table pageindex 3 because neon forms no covalent or ionic compounds and hence its radius is difficult to measure. The effective nuclear charge often symbolized as or is the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a polyelectronic atom the term effective is used because the shielding effect of negatively charged electrons prevents higher orbital electrons from experiencing the full nuclear charge of the nucleus due to the repelling effect of inner layer electrons. Periodic trends and effective nuclear charge zeff examples.
Which element has the larger zeff value.
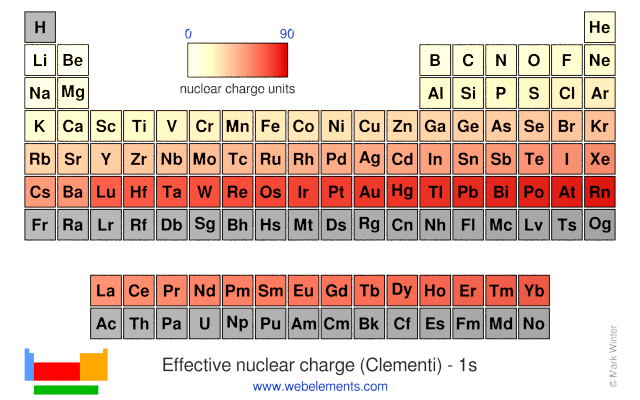
Which element has the larger zeff value. Periodic trends and effective nuclear charge zeff examples. The effective nuclear charge often symbolized as or is the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a polyelectronic atom the term effective is used because the shielding effect of negatively charged electrons prevents higher orbital electrons from experiencing the full nuclear charge of the nucleus due to the repelling effect of inner layer electrons.
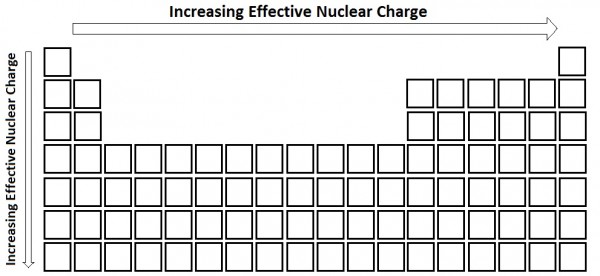
The neon atom in this isoelectronic series is not listed in table pageindex 3 because neon forms no covalent or ionic compounds and hence its radius is difficult to measure. Consequently the ion with the greatest nuclear charge al 3 is the smallest and the ion with the smallest nuclear charge n 3 is the largest.