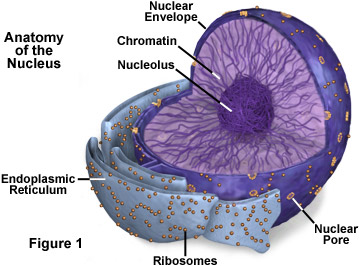
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Start studying mtc interphase nucleus lecture block 1. The inner layer of the bi layer facing the nucleoplasm is anchored to the nuclear lamina via nuclear pores.

The outer side of the bi layer facing the cytoplasm is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. The nuclear envelope aka nuclear membrane is the outer layer of the nucleus. In the textbook view it somehow arises as a consequence of phosphorylation of lamins and components of the nuclear envelope such as the nucleoporins.

Nuclear envelope breakdown is a fundamental feature of the cell cycle in most animal cells and yet its basis remains poorly understood. Furthermore nuclear membrane is a lipid bilayer while nuclear envelope consists of two nuclear membranes and nuclear pores. The main difference between nuclear membrane and nuclear envelope is that the nuclear membrane is the selective barrier between the nucleoplasm and cytoplasm whereas the nuclear envelope is the structure that separates the content of the nucleus from the cytoplasm.

However this notion has been questioned recently. Net release was described as a cellular lysis process. Nuclear envelope rupture and chromatin externalization is a hallmark of the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps nets.

The nuclear lamina is essential for the structural integration of the nuclear envelope. However nuclear envelope breakdown is. Nuclear lamin b is a substantial component of nuclear envelope that is involved in neutrophil netosis neutrophils are terminally differentiated cells and the role of nuclear lamina in neutrophil biology is not well understood olins et al 2008.

The nuclear lamina is a meshwork of nuclear intermediate filaments formed by a and b type lamins located primarily near the inner membrane of the nuclear envelope but also found at low levels within the nucleoplasm dittmer misteli 2011. An internal network forms the nuclear lamina on the inner nuclear membrane. Two sets of intermediate filaments provide support for the nuclear envelope.

These membranes are connected to each other by nuclear pores.
Nuclear lamina vs nuclear envelope. The nuclear lamina is a dense 30 to 100 nm thick fibrillar network inside the nucleus of most cells it is composed of intermediate filaments and membrane associated proteins besides providing mechanical support the nuclear lamina regulates important cellular events such as dna replication and cell division additionally it participates in chromatin organization and it anchors the nuclear. Nuclear envelope nuclear lamina and inherited disease. Worman hj 1 courvalin jc. 1 department of medicine and department of anatomy and cell biology college of physicians and surgeons columbia university new york new york 10032 usa.
The nuclear envelope is composed of the nuclear membranes nuclear lamina and nuclear pore complexes. The nuclear envelope is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes. An inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane.

An inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. The nuclear envelope is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes. The nuclear envelope is composed of the nuclear membranes nuclear lamina and nuclear pore complexes.

1 department of medicine and department of anatomy and cell biology college of physicians and surgeons columbia university new york new york 10032 usa. Worman hj 1 courvalin jc. Nuclear envelope nuclear lamina and inherited disease.

The nuclear lamina is a dense 30 to 100 nm thick fibrillar network inside the nucleus of most cells it is composed of intermediate filaments and membrane associated proteins besides providing mechanical support the nuclear lamina regulates important cellular events such as dna replication and cell division additionally it participates in chromatin organization and it anchors the nuclear.