Download the supplementary information. Analysis and prediction of leucine rich nuclear export signals tanja la cour lars kiemer anne mølgaard ramneek gupta karen skriver and søren brunak protein eng. Leucine rich nuclear export signal prediction software tools protein sequence data analysis leucine rich nuclear export signals ness are short amino acid motifs that mediate binding of cargo proteins to the nuclear export receptor crm1 and thus contribute to regulate the localization and function of many cellular proteins.

The nuclear export of proteins is regulated largely through the exportin crm1 pathway which involves the specific recognition of leucine rich nuclear export signals ness in the cargo proteins and modulates nuclear cytoplasmic protein shuttling by antagonizing the nuclear import activity mediated by importins and the nuclear import signal nls. Xpo1 mutations alter nuclear export signal recognition in a sequence specific manner and sensitize cells to compounds in clinical development inhibiting xpo1 function. Here we identify that heterozygous mutations in the main nuclear exporter in eukaryotic cells xpo1 are positively selected in cancer and promote the initiation of clonal b cell malignancies.

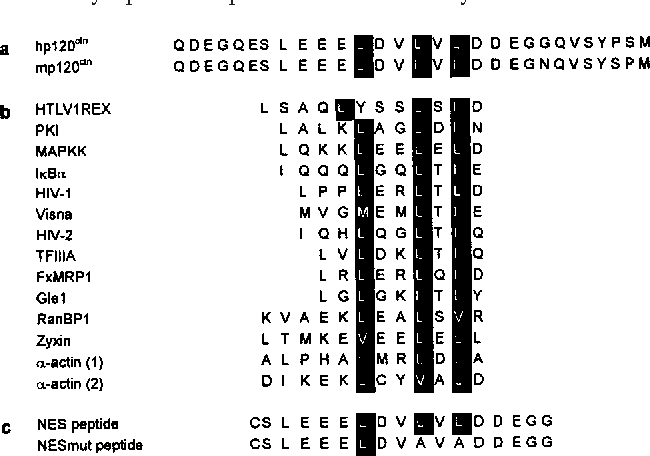
A signal sequence encoded in a protein that causes nuclear import is recognized as the nuclear localization signal nls whereas the sequence that causes nuclear export is called the nuclear export signal nes. The consensus pattern of nuclear export signal nes is a short sequence motif that is commonly identified in protein sequences whether the motif acts as an nes true positive or not false positive. We analyzed the sequences and three dimensional structures of natural experimentally identified ness and of false positive ness that were generated from the database in order to identify properties that might distinguish the two groups of sequences.

We compiled 200 nuclear export signal nes containing crm1 cargoes in a database named nesdb. Different nuclear localized proteins may share the same nls. A nuclear localization signal or sequence nls is an amino acid sequence that tags a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport typically this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines or arginines exposed on the protein surface.
The putative nls in exon 15 was initially thought to be the authentic nls but subsequent studies demonstrated that it fails to function. The nuclear localization signal nls in exon 1 the nuclear export signal nes in exon 3 and the caspase cleavage site amino acids 256 307 in exon 3 are labeled. A nuclear export signal nes is a short target peptide containing 4 hydrophobic residues in a protein that targets it for export from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm through the nuclear pore complex using nuclear transport it has the opposite effect of a nuclear localization signal which targets a protein located in the cytoplasm for import to the nucleus.